Ravva Fm
Type Locality and Naming
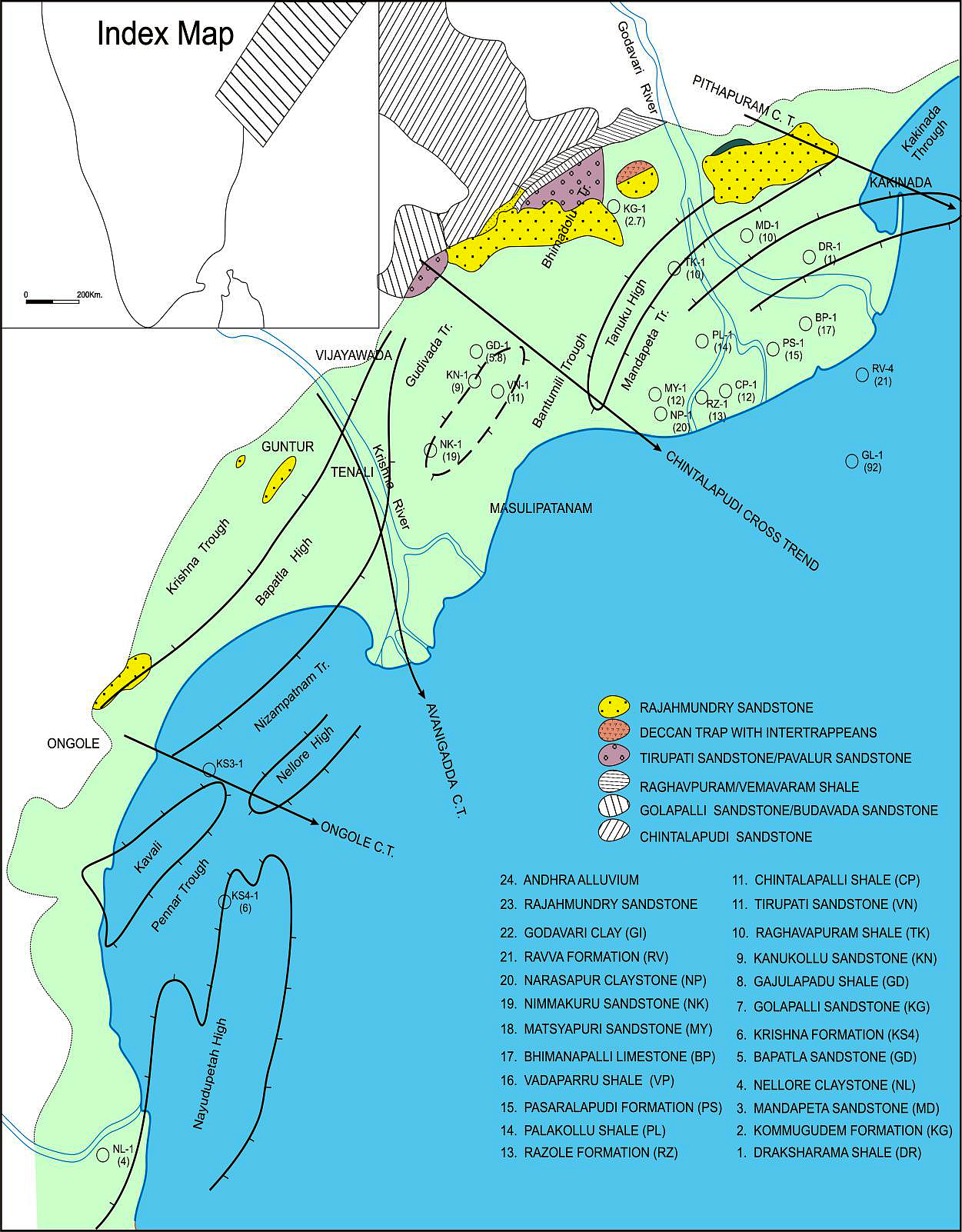
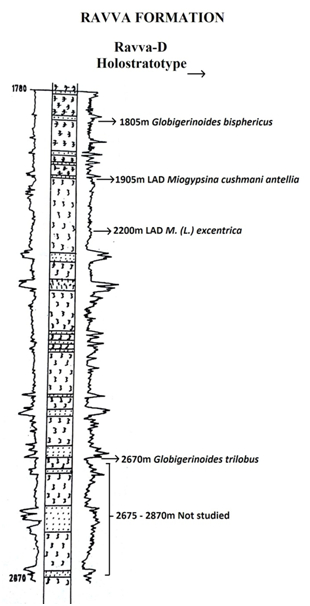
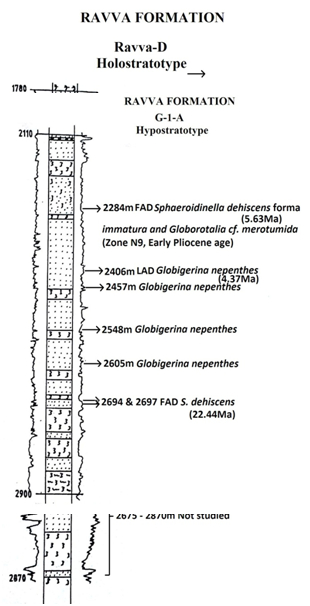
BASINAL: The type section is in the Well Ravva-D (depth interval: 1780-2870 m). The hypostratotype is in the Well G-A-A (depth interval: 2110-2900 m). It was named after Ravva by ONGC team steered by Venkatarengan et al. (1993) adopted and issued as Document-VII by KDMIPE, ONGC, Dehradun (1993). [Original Publication: Rao, G.N. (1990) Subsurface stratigraphic nomenclature of Krishna-Godavari Basin, ONGC, unpublished report.]. Reference well: Well G-1-1, Interval 2110-2900 m and thickness is 790 m.
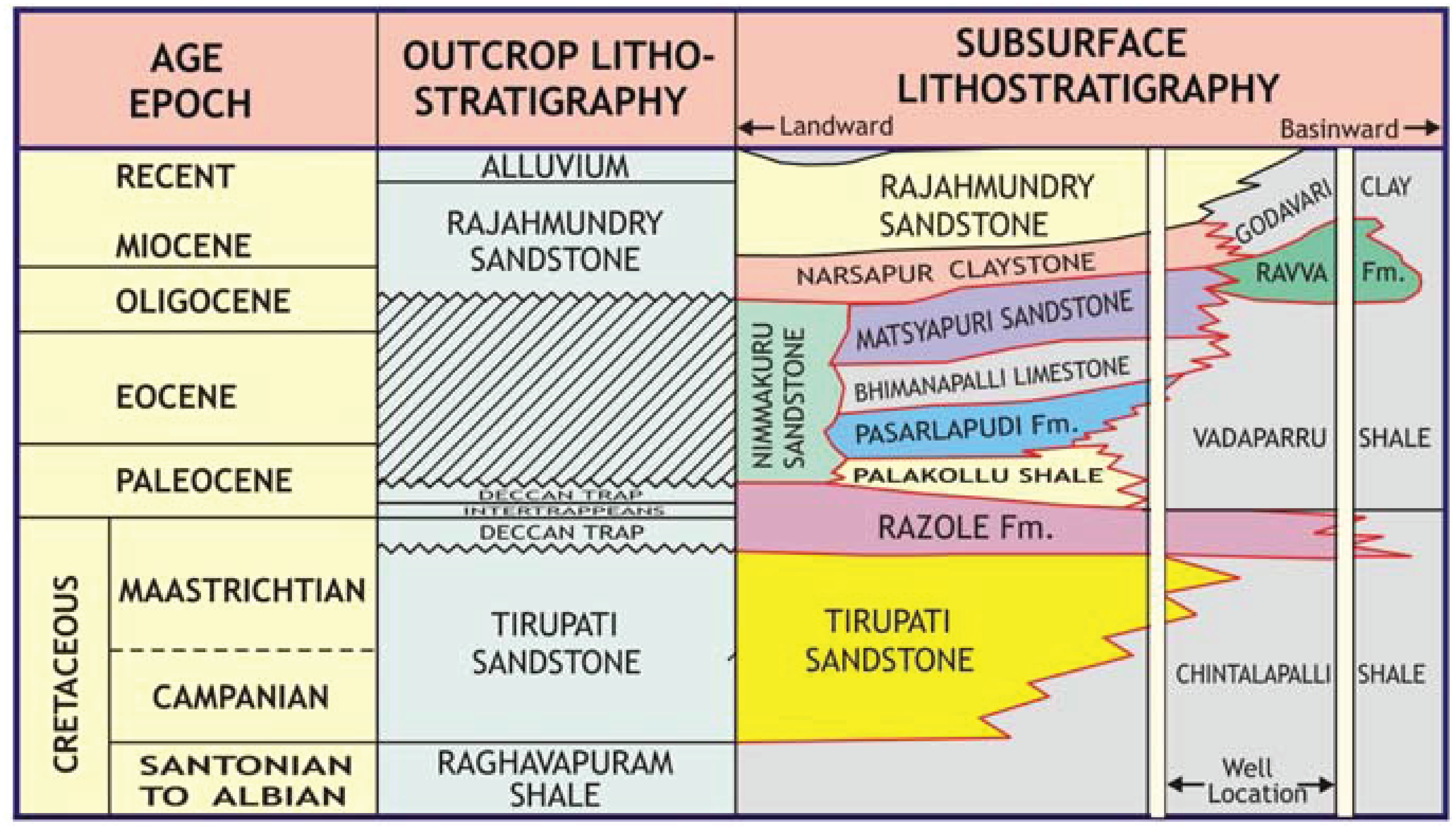
[Figure: Generalized Late Cretaceous-Cenozoic lithostratigraphy transect, Krishna-Godavari Basin. From Keller et al., 2011, Jour. Geol. Soc. India, 78:399-428, their Fig. 2]
[Figure: Map showing the locations of designated holostratotype section for the formation in the KG Basin (After ONGC, Pandey and Dave, 1998) in Raju et al., 2021, ONGC Bulletin, Special Issue, Vol. 56, No. 2]
Lithology and Thickness
Clayey sandstone. In the type section (well in Ravva-D), the formation consists of thin sandstone beds alternating with thick clay beds and minor siltstone layers. The sandstone in the section is argillaceous sometimes pebbly, ill sorted. At the contact with the claystone, the sand is mostly glauconitic and calcareous, associated claystone is mostly pyritiferous, sometimes silty, calcareous, with slight fissility. In the reference section (well G-A-A), it is sandstone and claystone alternation. The sandstone is grey to dark grey, fine to medium grained. The claystone is dark grey, moderately hard, compact and at places with pyrite. At places claystone is silty. It has a thickness varying from 790-990m.
[Figure 1: Well log of Ravva-D Holostratotype (modified after Venkatarengan et al., 1993)]
[Figure 2: Well log of G-1-A Hypostratotype (modified after Venkatarengan et al., 1993)]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Conformable with Narasapur Fm Claystone. Or Unconformable with the Matsyapuri Fm Sandstone.
Upper contact
Unconformable with the Godavari Fm.
Regional extent
It is extensively developed in parts of Krishna-Godavari Basin. Partly coeval with Rajahmundry Fm (which is more landward).
GeoJSON
Fossils
Foraminifera – Globigerinoides sicanus, Gs. trilobus, Gs. primordius, Praeorbulina transitoria, P. glomerosa, Globorotalia periphororonda, Gr. siakensis, Globoquadrina altispira altispira, Gq. altispira globosa, Miogypsina (L) excentrica, Lenticulina, Uvigerina (costate). Ichnofossils – Skolithos, Ophiomorpha, Thalassinoides, Planolites and Paleophycus.
Age
Depositional setting
Inner-Middle neritic.
Additional Information
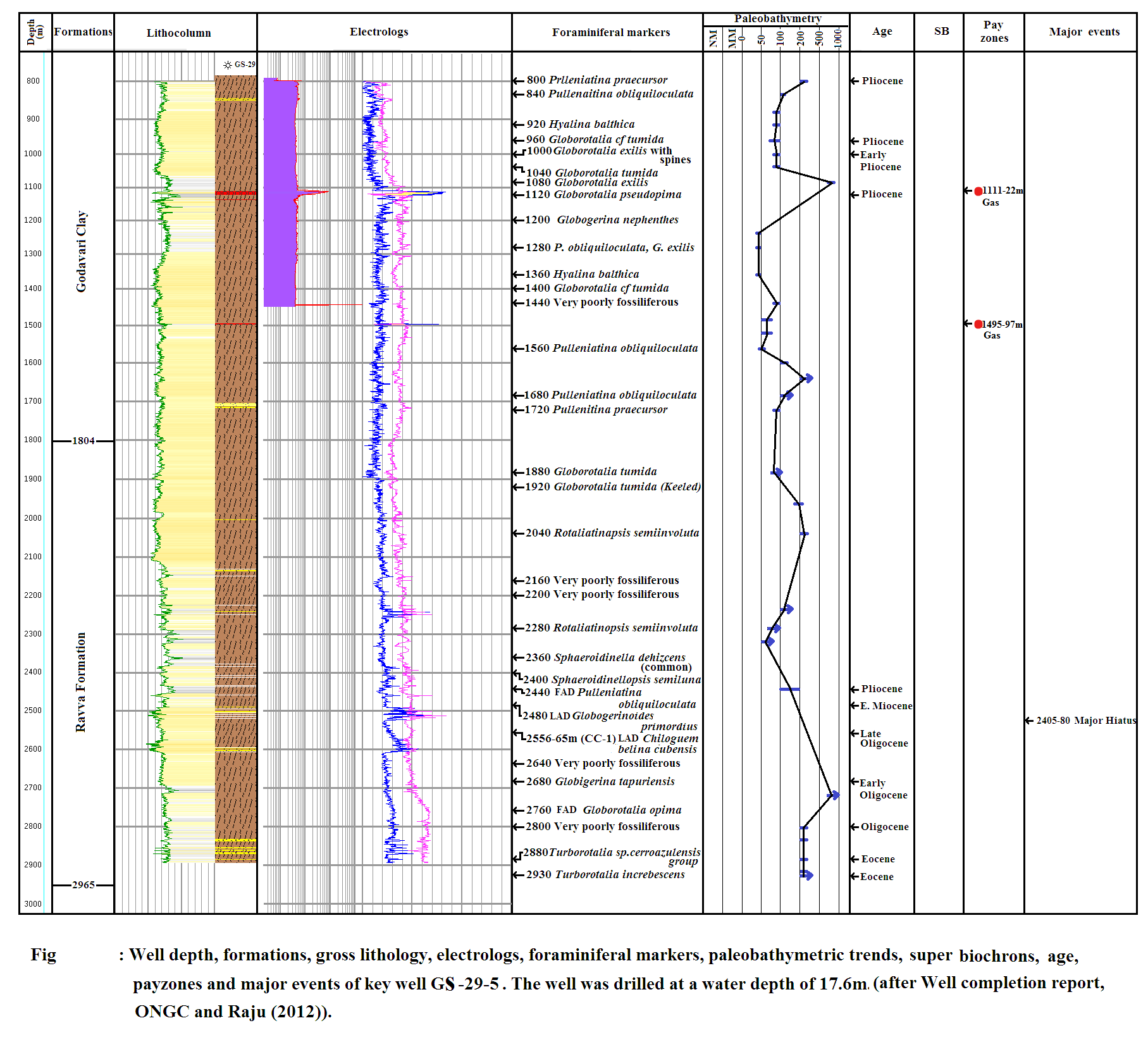
[Figure 3: Lithocolumn, well logs, foraminiferal datums and paleobathymetry of Ravva Fm in well GS-29-5 showing lateral variation (after well completion report, ONGC and Raju (2013)]